1 | P a g e
Kick Off Activity
Classification of Igneous Rocks (Pg. 2)
The Foundation
Igneous Reading with Question Sheet (Pg. 3-5)
Scheme for Igneous Rock Identification – ESRT Page 6
Video: Mr. White’s Website Questions: In Packet (Pg. 6-8)
ESRT Page 6 Practice (Pg. 9-10)
Hands–On
Igneous Rock Identification Lab (Pg. 11-14)
Tune-Up Activities
Crossword Puzzle (Pg. 15)
Flashcards (In Classroom)
Igneous Rocks Review Sheet (Pg. 16-17)
Online Self-Check Quiz ( Mr. White’s Website)
Check For
Understanding
Quizzes
SCORE: Quiz 1 _______ Quiz 2 _______ Quiz 3 _______
*You must get a 100% on a quiz to move on to extension activities.
*A 100% on a quiz will earn you a grade of 80% for the workbook.
Extension
Activities
Bowen’s Reaction Series (Pg. 18-19 )
The Granite Countertop (Pg. 20)
The Company of Rocks (Pg. 21-22)
Composition of Igneous Rocks - PowerPoint (Pg. 23 )
Regents Diagrams-What are they telling me (Pg. 24-26)
NAME: _______________________
5 Pts.
5 Pts.
10 Pts.
5 Pts.
MUST DO ALL
DO AT LEAST 2
If you didn’t get
100%, do more
tune-ups!!!
5 Pts.
2 | P a g e
Igneous Rock Classification
1. What properties did you use to classify (group) the igneous rocks?
Group #1 - ____________________________________________
Group #2 - _____________________________________________
Group #3 - _____________________________________________
Wait for teacher direction to complete table below…

3 | P a g e
Igneous Rocks
How Igneous Rocks Form
Igneous rocks form from the solidification and crystallization of
molten (melted/liquid) rock, making the rocks solid, compact, and
hard. Beneath the Earth’s surface, molten rock material is called
magma. When the magma reaches the Earth’s surface, it is called
lava. When magma or lava cools and solidifies, mineral crystals
may form, resulting in the igneous rock having a crystalline
texture. Usually there are many different minerals within this
kind of rock.
QUESTIONS:
1. How do igneous rocks form?
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
2. Compare and contrast magma and lava.
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
Texture
The texture of the igneous rocks is dependent upon the rate of
cooling. Slow cooling produces large crystals – rocks with a
coarse texture. Rapid cooling produces small crystals – rocks
with a fine texture. When bubbles of gas are in solidifying
lava, holes called vesicles, are formed. Igneous rocks that
contain these holes are said to be vesicular.
QUESTIONS:
1. What determines the texture of an igneous rock?
_____________________________________________________________________________
2. State the relationship between cooling rate and crystal size.
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
3. If an igneous rock has a “coarse texture,” what would you see?
_____________________________________________________________________________
4. What are vesicles? _____________________________________________________________
Vesicular Igneous Rock
4 | P a g e
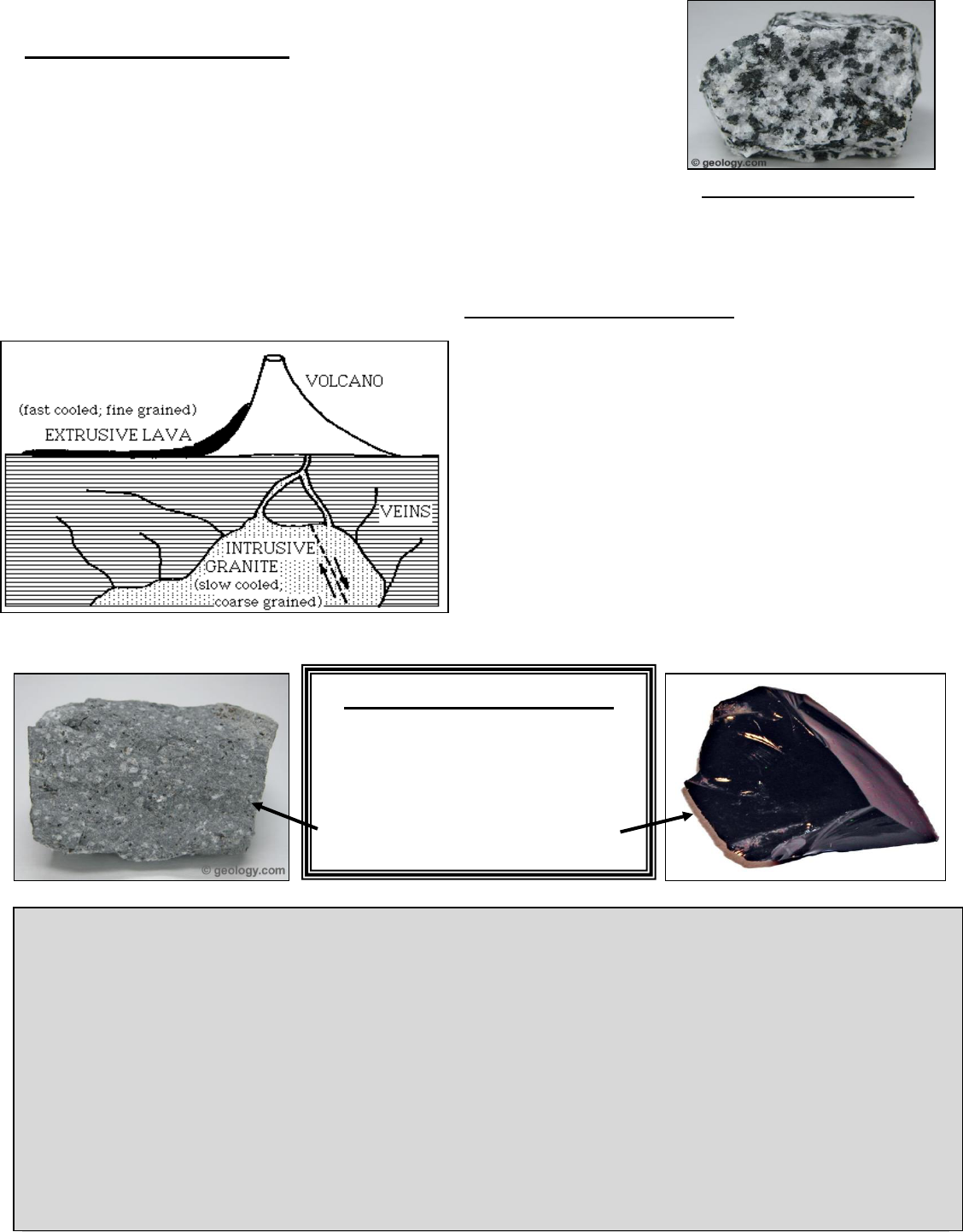
Intrusive Igneous Rocks
Cooling is related to both temperature and pressure. Deep within the
Earth both temperature and pressure are much greater than at the
surface. Therefore, cooling is slower and crystals have more time to
grow larger. When magma hardens inside the Earth, it is called an
intrusion. The rock formed is called an intrusive igneous rock.
By looking at the size of the crystals in igneous rocks, you can
estimate their relative cooling rates.
Extrusive Igneous Rocks
Rapid (fast) cooling produces small mineral crystals
and a fine textured igneous rock. Very rapid cooling
prevents the formation of crystals and gives the rock a
glassy texture. The conditions for a rapid decrease in
temperature and pressure exist at the surface of the
Earth when lava breaks through the surface during a
volcanic eruption. When lava flows out and hardens
on the Earth’s surface, it is called an extrusion. The
rock formed is called an extrusive igneous rock.
QUESTIONS:
1. Where do intrusive igneous rocks form? __________________________________________
2. Describe the cooling rate, crystal size, and texture of intrusive igneous rocks:
Cooling rate: _____________________ Crystal Size: ______________________
Texture: _______________________________
3. Where do extrusive igneous rocks form? __________________________________________
4. Describe the cooling rate, crystal size, and texture of extrusion igneous rocks:
Cooling rate: _____________________ Crystal Size: ______________________
Texture: _______________________________
Intrusive Igneous Rocks
slow cooling = large crystals and
a coarse texture
Extrusive Igneous Rocks
fast cooling = small or no
crystals.
Fine Texture or Glassy Texture

5 | P a g e
Properties of Igneous Rocks
Texture, color, density, and mineral composition are used to
identify igneous rocks. The light colored rocks are made
primarily of felsic minerals such as biotite. Felsic minerals
contain a lot of aluminum and silicon. Aluminum is light in color
and has a low density. As a result, light colored rocks are lower
in density than darker rocks. Dark colored rocks are made
primarily of mafic minerals such as olivine. Mafic minerals are
rich in iron and magnesium which causes darker rocks to be
denser.
QUESTION:
1. Why are light colored igneous rocks usually less dense
than dark colored igneous rocks?
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
Where are they found?
Igneous rocks are common in both the continental and oceanic crust of the Earth. Low density, felsic
igneous rock (granite) is common in the continental crust. Oceanic crust is made primarily of high
density, mafic igneous rock (basalt).
QUESTIONS:
1. What type of igneous rock is most common in the
continental crust?
________________________________________
2. What type of igneous rock is most common in the
oceanic crust?
________________________________________
Felsic
(low density)
Mafic
(high density)

6 | P a g e
Scheme for Igneous Rock Identification Video and Questions
The Scheme for Igneous Rock Identification chart (ESRT page 6) can be used to identify igneous
rocks. It can also be used to gather additional information about a rock you have already identified.
The texture, mineral composition, density, crystal size, etc… of an igneous rock is located in the table.
Follow the stared steps to complete this section
You will be watching a video to learn about ESRT page 6. Use a computer to access
Mr. White’s website. Access the video by clicking on the link for IGNEOUS ROCK ONLINE
RESOURCES. Be sure to follow the directions carefully and pause the video at the right time
to answer questions.
Watch the video from the BEGINNING and PAUSE it when you reach the time of 2:25.
Use what you have just learned and the ESRT to answer the questions that follow. Replay this
portion of the video if you need to watch it again!
Using ESRT page 6, you can determine igneous rock texture and environment
of formation based on crystal size.
1. Rocks with a crystal size of 10mm or larger = _______________________ texture.
2. Rocks with a crystal size of 1mm to 10mm = ________________________ texture.
3. Rocks with a crystal size of less than 1mm = ________________________ texture.
4. Rocks without crystals (non-crystalline) = ________________________ texture.
5. What’s another term for INTRUSIVE? ________________ EXTRUSIVE?_______________
6. Describe 3 differences between extrusive and intrusive igneous rocks?
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
1
2

7 | P a g e
Watch the video from 2:25 and PAUSE it when you reach the time of 3:15. Then use what
you have just learned and the ESRT to answer the questions that follow. Replay this portion of
the video if you need to watch it again!
Using ESRT page 6, you can determine if an igneous rock is mafic or felsic,
high in density or low in density, and light in color or dark in color.
1. Describe the color, density, and composition of the rocks on the LEFT side of the chart.
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
2. Describe the color, density, and composition of the rocks on the RIGHT side of the chart.
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
Watch the video from 3:15 and PAUSE it when you reach the time of 4:45. Then use what
you have just learned and the ESRT to answer the questions that follow. Replay this portion of
the video if you need to watch it again!
Using ESRT page 6, you can determine the mineral composition of an igneous rock.
1. Write the 5 minerals that make up the igneous rocks on the LEFT SIDE of the chart.
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
2. Write the 5 minerals that could be in the igneous rocks located in the MIDDLE of the chart.
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
3. Write the 5 minerals that could make up the igneous rocks on the RIGHT SIDE of the chart.
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
3
4
3

8 | P a g e
Watch the video from 4:45 until the end. Then use what you have just learned and the ESRT
to answer the questions that follow. Replay this portion of the video if you need to watch it
again!
Check Your Understanding:
1. Which igneous rock has crystal size of less than 1 mm and is light in color? ____________________
2. What is the texture of the rock you named in question 1? _________________________
3. Is the rock intrusive or extrusive? ______________________
4. Is the rock mafic or felsic? __________________ High density or low density? _____________
5. List the minerals that make up the rock. ______________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________
5

9 | P a g e
ESRT Page 6 Practice

10 | P a g e
11 | P a g e
Igneous Rock Identification Lab
Introduction: Igneous rocks, also called volcanic rocks, are interesting to study. They can be
coarse gained ( intrusive ) or fine gained ( extrusive ). This texture is dependent on a rock’s rate
of cooling. They can also be light in color, intermediate in color, or dark in color. The color tells
you what minerals are present in the rock. Page 6 of your reference tables is essential for your
successful completion of this lab.
Materials: ESRT, Igneous rocks, cranial space full of gray matter.
Procedure:
1. You will be identifying 7 different igneous rocks in this lab. You must have your
EARTH SCIENCE REFERENCE TABLES ready before you can get your rock samples.
2. For PART 1, you will use a check list to help you identify 3 igneous rocks.
3. For PART 2, you will fill in a data table with the correct properties for rocks 4-7. You
will then use those properties to identify the rocks.
4. Answer all questions.
The following is a list of ways that you can improve your science lab
write-ups.
I used complete sentences when appropriate.
I answered all questions with complete ideas.
I am neat, including using a pencil to erase mistakes.
I reviewed the lab to make sure all questions are answered correctly.
I asked the teacher for help when needed.

12 | P a g e
Part 1: Select one rock at a time from the back of the classroom. Fill in or check the spaces in
the following chart for each of the rock samples.
ROCK 1 (check all that apply)
Color: ____ Dark ____Intermediate ____Light
Texture: ____ Coarse ____Fine ___ Glassy
____ Vesicular ____ Non-Vesicular
Rock Name: ________________________
3 possible minerals present: _____________ ______________ _____________
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ROCK 2 (check all that apply)
Color: ____ Dark ____Intermediate ____Light
Texture: ____ Coarse ____Fine ___ Glassy
____ Vesicular ____ Non-Vesicular
Rock Name: ________________________
3 possible minerals present: _____________ ______________ _____________
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ROCK 3 (check all that apply)
Color: ____ Dark ____Intermediate ____Light
Texture: ____ Coarse ____Fine ____Glassy (Glassy means no mineral crystals)
____ Vesicular ____ Non-Vesicular
Rock Name: ________________________
3 possible minerals present: _____________ ______________ _____________
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------

13 | P a g e
Part 2: Use your ESRT to identify the rocks below.
Igneous Rock Data Table
Rock #
Color
(light, intermediate,
or dark)
Texture
(glassy, fine, coarse,
vesicular, non-vesicular)
Intrusive
or
Extrusive
Mafic (oceanic)
or
Felsic (continental)
Rock Name
4
5
6
Dark in
color but
Felsic
7
Intermediate
(between Mafic and Felsic)
Questions: Answer the following questions.
1. How is the formation of intrusive igneous rocks different from the formation of extrusive
igneous rocks form?
___________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
2. What is the relationship between cooling rate of igneous rocks and their crystal size?
The longer the cooling time, the ___________________ the mineral crystal size.
OVER FOR MORE

14 | P a g e
3. How are the rocks gabbro and granite similar?
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
4. Which 3 minerals do basalt and granite have in common?
________________________________________________________________________
5. Which rock will form if magma cools and hardens deep below the Earth’s surface
and contains only the minerals pyroxene and olivine?
_______________________________

15 | P a g e

16 | P a g e
Igneous Rock Review Sheet
Formation of Igneous Rocks
Match each description to its term.
Description Term
_____1. the meaning of the Latin a. magma
word ignis
_____2. rocks that form when magma b. granite
hardens beneath Earth’s surface
_____3. rocks that form when lava hardens c. intrusive igneous
_____4. melted material beneath Earth’s d. lava
surface
_____5. melted material at Earth’s surface e. rhyolite
_____6. an intrusive igneous rock that f. fire
forms when magma cools slowly
beneath Earth’s surface
_____7. an extrusive igneous rock that g. extrusive igneous
forms when lava cools quickly
at Earth’s surface
Classification of Igneous Rocks
1. Give two characteristics used to classify igneous rocks are:
_________________________ and _________________________
2. Is the following sentence true or false?
Igneous rocks that are composed primarily of quartz and feldspar have a felsic
composition. ______________________

17 | P a g e
3. Circle the minerals that are found in andesite.
a. amphibole c. pyroxene e. olivine
b. biotite d. plagioclase feldspar f. potassium feldspar
4. Peridotite is composed almost entirely of dark silicate minerals. Its chemical composition
is referred to as ______________________.
5. Circle the statements that are TRUE about the texture of igneous rocks.
a. Slow cooling results in rocks with small, interconnected mineral grains.
b. Rapid cooling of magma or lava results in rocks with small, interconnected
mineral grains.
c. A glassy texture is the result of lava that has cooled very slowly.
d. Vesicular rocks have gas pocket holes.
e. Glassy rocks are non-crystalline.
6. Describe 2 ways GRANITE is different than BASALT.
7. How is continental crust different from oceanic crust?

18 | P a g e
Bowen’s Reaction Series
Norman Bowen was a scientist who studied how igneous rocks formed. He experimented with
laboratory melts of igneous rocks in the 1920s and 1930s and discovered an experimental
crystallization sequence of minerals that matched what was observed in nature. Bowen ground up
actual igneous rocks, along with mixtures of chemicals, and melted them in a very strong container
under high temperatures and pressures. Like all igneous rocks that form from liquid magma or lava,
Bowen’s experimental samples formed igneous rocks and how they formed with various compositions
is outlined in the chart below. Depending on the original melt’s composition, how fast it cooled and if
any elements where removed during cooling, different igneous rocks with different compositions will
form.
Questions
1. Describe what the chart above is illustrating. Be specific with details.
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
OVER
1200°C
600°C
Form at
higher
pressure
Form at
lower
pressure

19 | P a g e
2. In any good experiment there is an independent variable and a dependent variable that a
scientist is studying. In Bowen’s reactions series, the independent variable is temperature.
What is the dependent variable? Explain your choice.
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
3. Describe the temperature and pressure conditions shown in Bowen’s Reaction Series that
explain why olivine and quartz are not usually found in the same igneous rock.
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
4. Using the chart, identify one similarity and one difference between the igneous rocks basalt
and andesite.
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
5. Granite and gabbro both form slowly deep underground. When brought to the surface of the
Earth, granite is more stable and lasts longer than gabbro. Why?
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
20 | P a g e
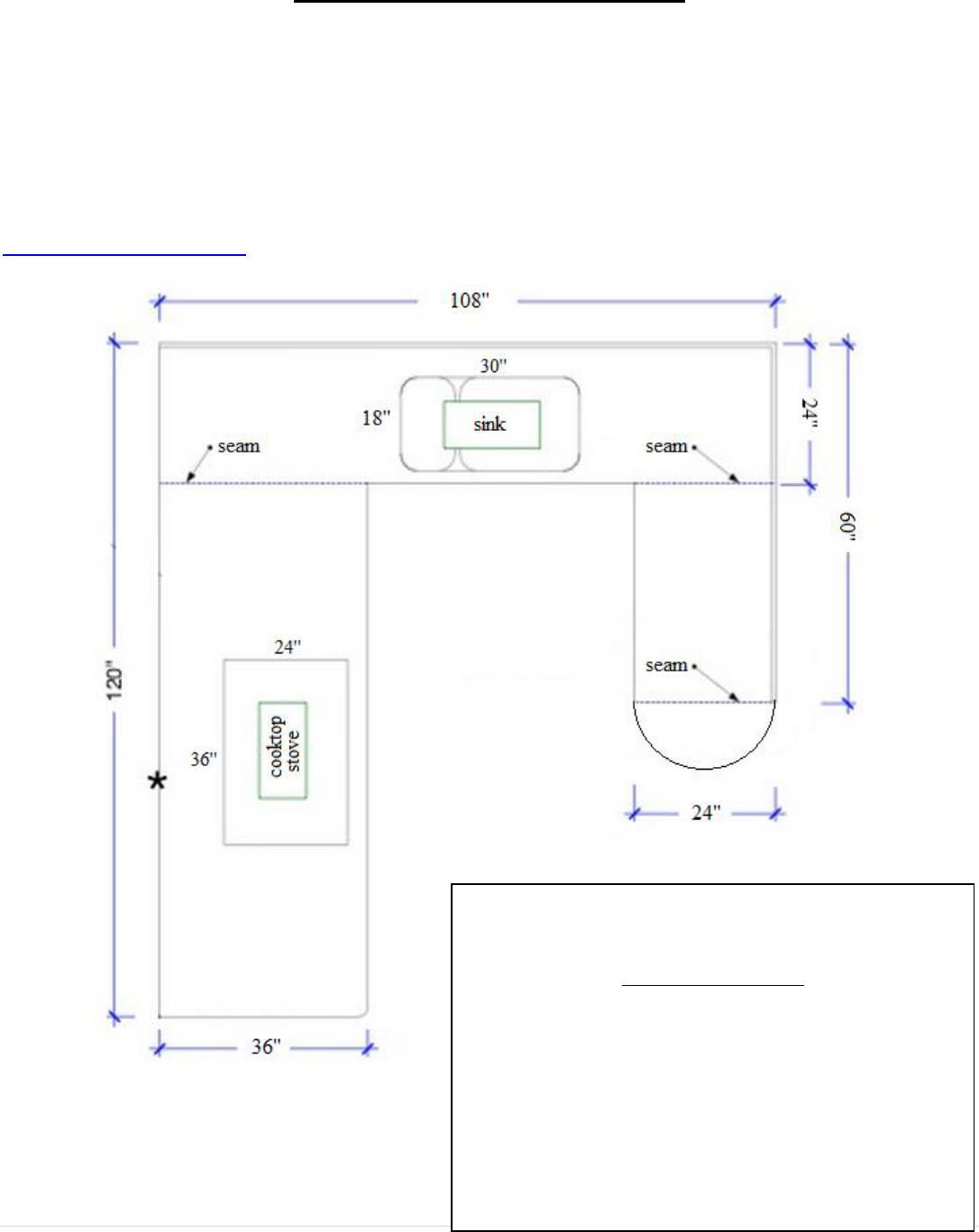
The Granite Countertop
You have been hired to determine the square footage and cost of the countertop outlined below. The
buyer wants to use granite for the countertop. Your task is to determine the minimum whole square
footage of granite needed and then provide quotes on the cost of 3 different types of granite
countertop. Make sure you take into account the area of the sink and cooktop stove when
determining your square footage. It is recommended that you convert the measurements below
from inches to feet before you calculate the surface area. You will need to do a little research to
determine the cost of granite per square foot. Check out this website to see some prices:
www.pacificgranitemn.com
Square Footage: ______________________
Granite Type and Cost
Include type of granite and cost for each quote below. You
can only purchase countertop in whole square feet. You will
have to round your square footage up first!
Low Cost Quote 1: __________________________________
Med Cost Quote 2: __________________________________
High Cost Quote 3: __________________________________

21 | P a g e

22 | P a g e
QUESTIONS – The Company of Rocks
1. What is the first thing that comes to mind after reading this article?
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
2. Compare the “lifespan” of a rock to the lifespan of a human (think time).
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
3. Find 2 terms that we have not seen in class. Define them.
1. ______________________ - ______________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
2. ______________________ - ______________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
4. The author tells a story about rocks. How do the rocks tell their own story?
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________

23 | P a g e
Directions
First, go through the
PowerPoint online. Then,
using the chart below, fill in
the percentages of the
minerals found in the rocks
indicated by each line.
Identify the density, color,
and composition of each
rock. Use your reference
tables for a clearer copy of
page 6.
Composition of Igneous Rocks with PowerPoint
%

24 | P a g e
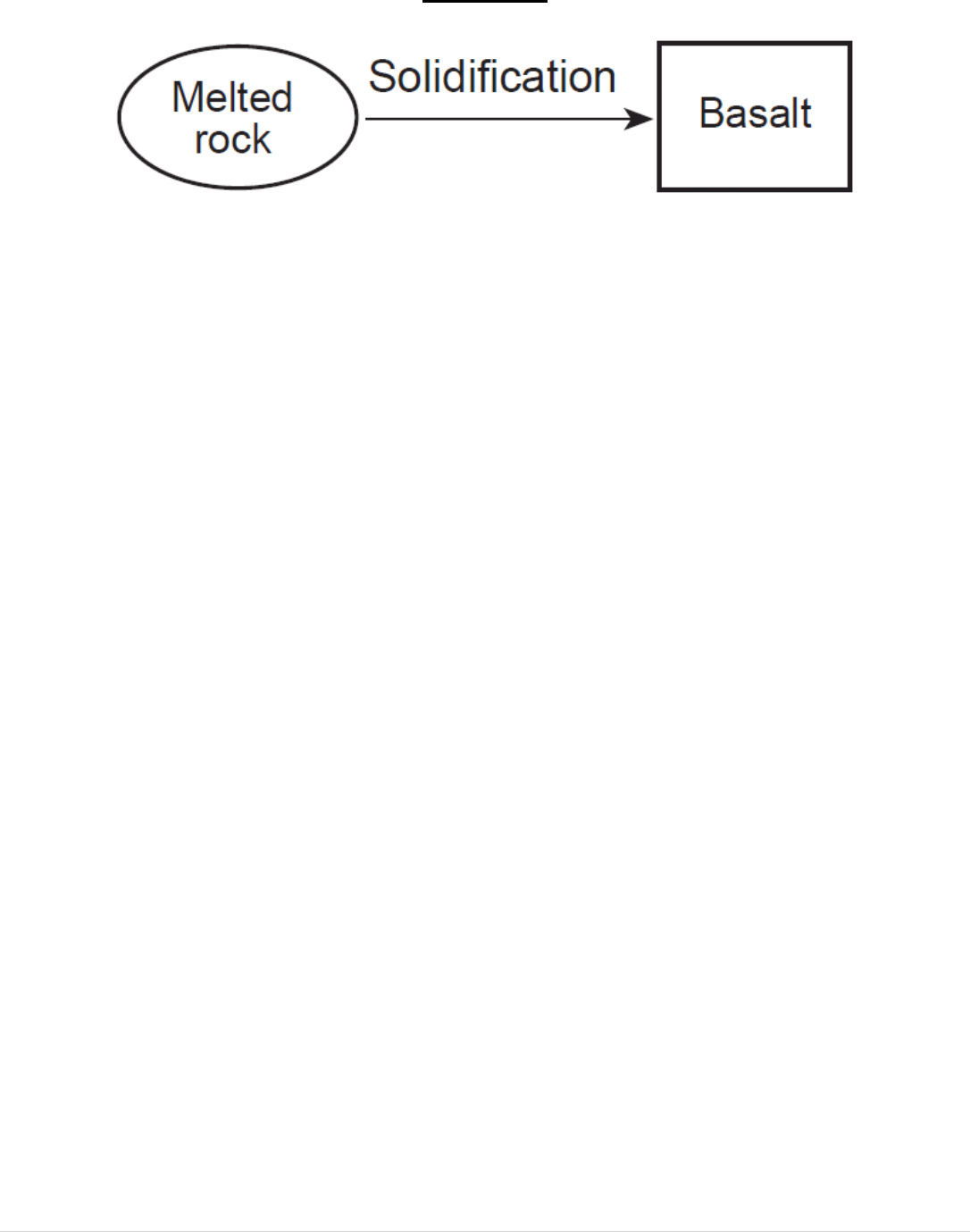
Igneous Rock Regents Diagrams- What are they telling me?
For each of the following diagrams, give an explanation of what you think the diagram is
showing. Then write one question the regents exam might ask you based on the diagram.
Diagram #1
Explanation:____________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
Question:
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
Diagram #2
Explanation:_______________________________
_________________________________________
_________________________________________
_________________________________________
_________________________________________
_________________________________________
________________________________________
Question:
_________________________________________
_________________________________________

25 | P a g e
Diagram #3
Explanation:__________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
Question:
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
Diagram # 4
Explanation:__________________________________________
____________________________________________________
____________________________________________________
____________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
Question:
____________________________________________________
____________________________________________________
____________________________________________________
Crystals
26 | P a g e
Diagram #5
Explanation:__________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
Question:
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
