
NAME _______________________ PER_____ DUE DATE _________________ MAIL BOX________
BRING COMPLETED REVIEW PACKET COMPLETE TO THE EXAM, THE DAY OF EXAM - RECEIVE 1 BONUS PT ON EXAM
Check your work, find answer key on website
ATOMS and THE PERIODIC TABLE
1. A unit of mass used to express atomic and molecular weights. One proton or
neutron equals one mass unit.
2. This is the center of atom. Most of the mass of the atom is here.
3. These are positively charged particles. They define an atom’s identity.
4. These are negatively charged particles. They define an atom’s reactivity.
5. These particles add to an atom’s mass.
6. The basic unit of a chemical element.
7. The mass of an atom of a chemical element expressed in atomic mass units. It is
approximately equivalent to the number of protons and neutrons in the atom (the
mass number) or to the average number. This why it is typically expressed with a
decimal.
8. Each of two or more forms of the same element that contain equal numbers of
protons but different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei, and hence differ in relative
atomic mass; in particular, a radioactive form of an element.
9. 10.
Matching
____ ATOM
____ATOMIC MASS
____ NUCLEUS
____ ISOTOPES
____ AMU
____ PROTONS
____ NEUTRONS
____ URANIUM
____ ELECTRONS
____ HYDROGEN
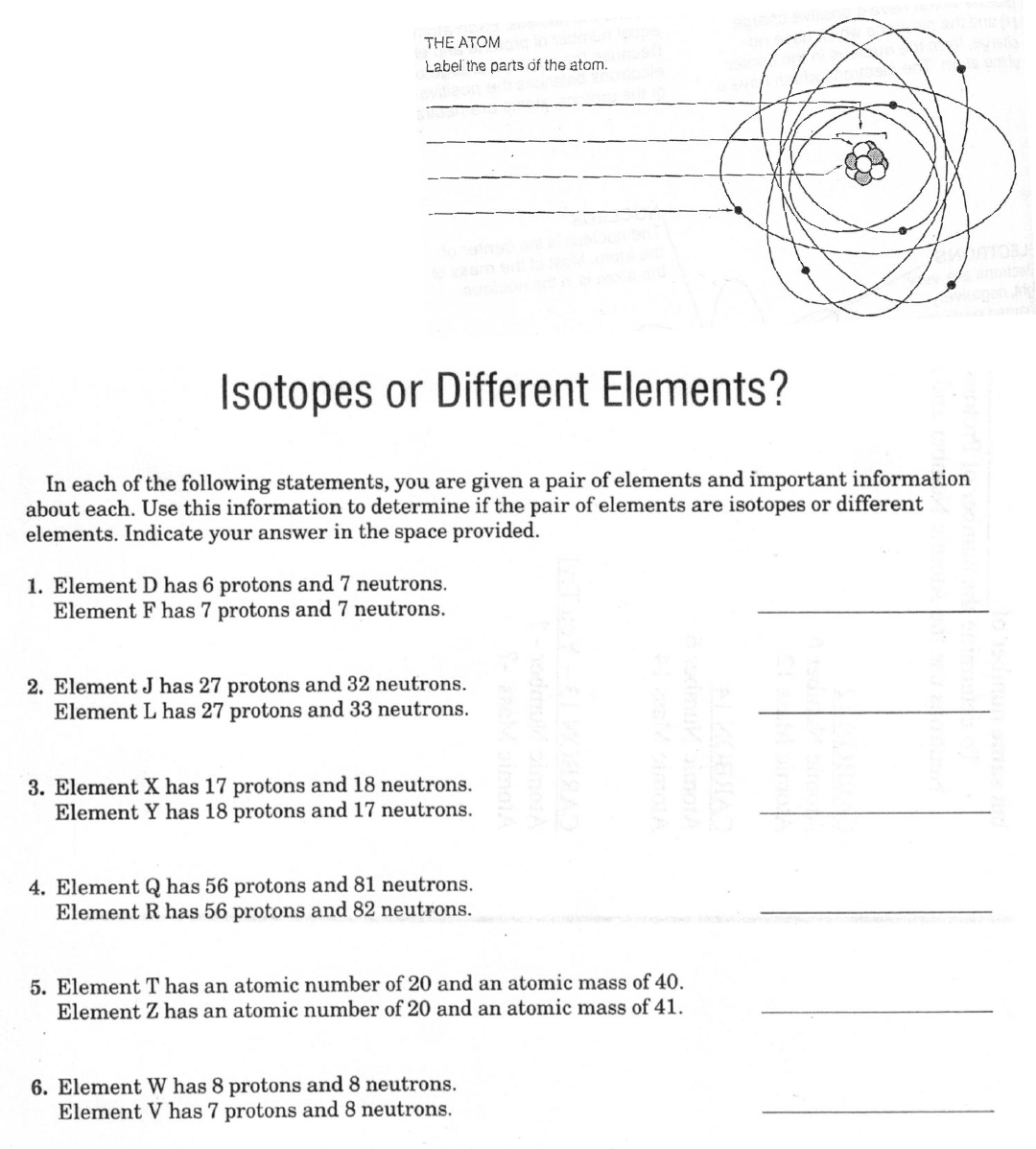
Read:
An atom is made of three basic particles; neutrons, protons and electrons. These are building blocks
of atoms are comprised of particles even smaller still such as quarks, leptons and neutrinos. Protons
have a positive charge and neutrons a neutral charge while together they make up the nucleus of an
atom. Varying numbers of protons (atomic number) give us the 94 or so naturally occurring elements
on earth. Varying numbers of neutrons simply effect atomic mass and give rise to different isotopes of
the same element. Atomic mass is the combined mass of both neutrons and protons. The electrons
which have a negative charge spin in
orbits around the nucleus. Each atom
has an equal number of protons and
electrons. Because, the negative
charge of the electrons balances the
positive charge of the protons, making
atoms typically neutral. Can you the
parts of this atom here? →
Atomic Theorems commit to memory, commit to memory
1. atomic number = proton count
2. proton count = electron count
3. atomic mass (minus) atomic number = neutron count
4. atomic mass = protons + neutrons
5. neutrons do not equal atomic mass
6. neutrons do not = electron count
-----------------------------------------------
7. Periods equal number of electron shells around nucleus
8. Groups equal number of valence electrons
7 & 8 Apply only to → (Alkali, Alkaline, BCNO Family, Nonmetals, Halogens and Noble Gases (not Transition Metals)
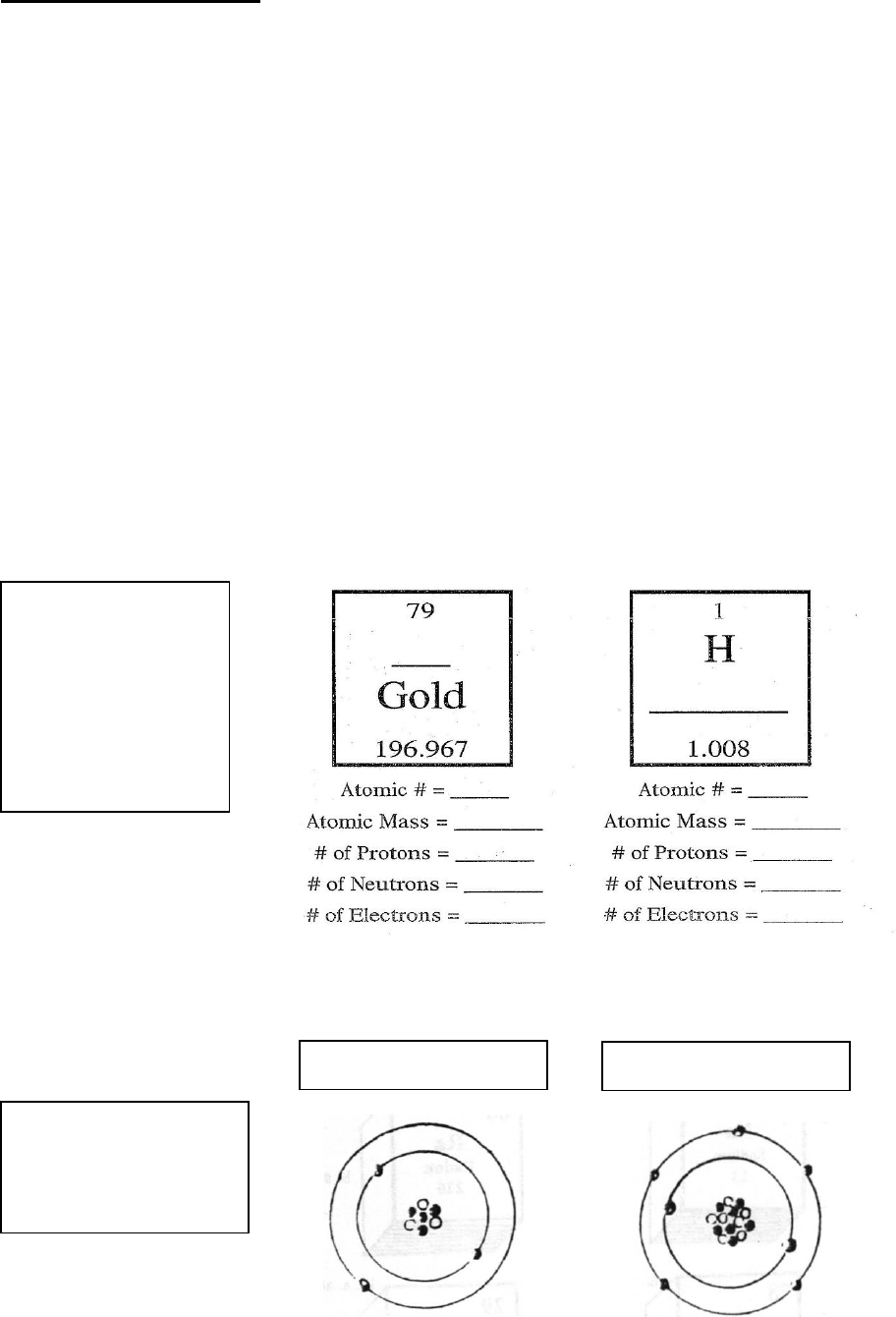
Using the Atomic
Theorems and a
Periodic Table these
should be easy
→ Fill in blank →
Using a Periodic Table
ID these atoms
→ Label→
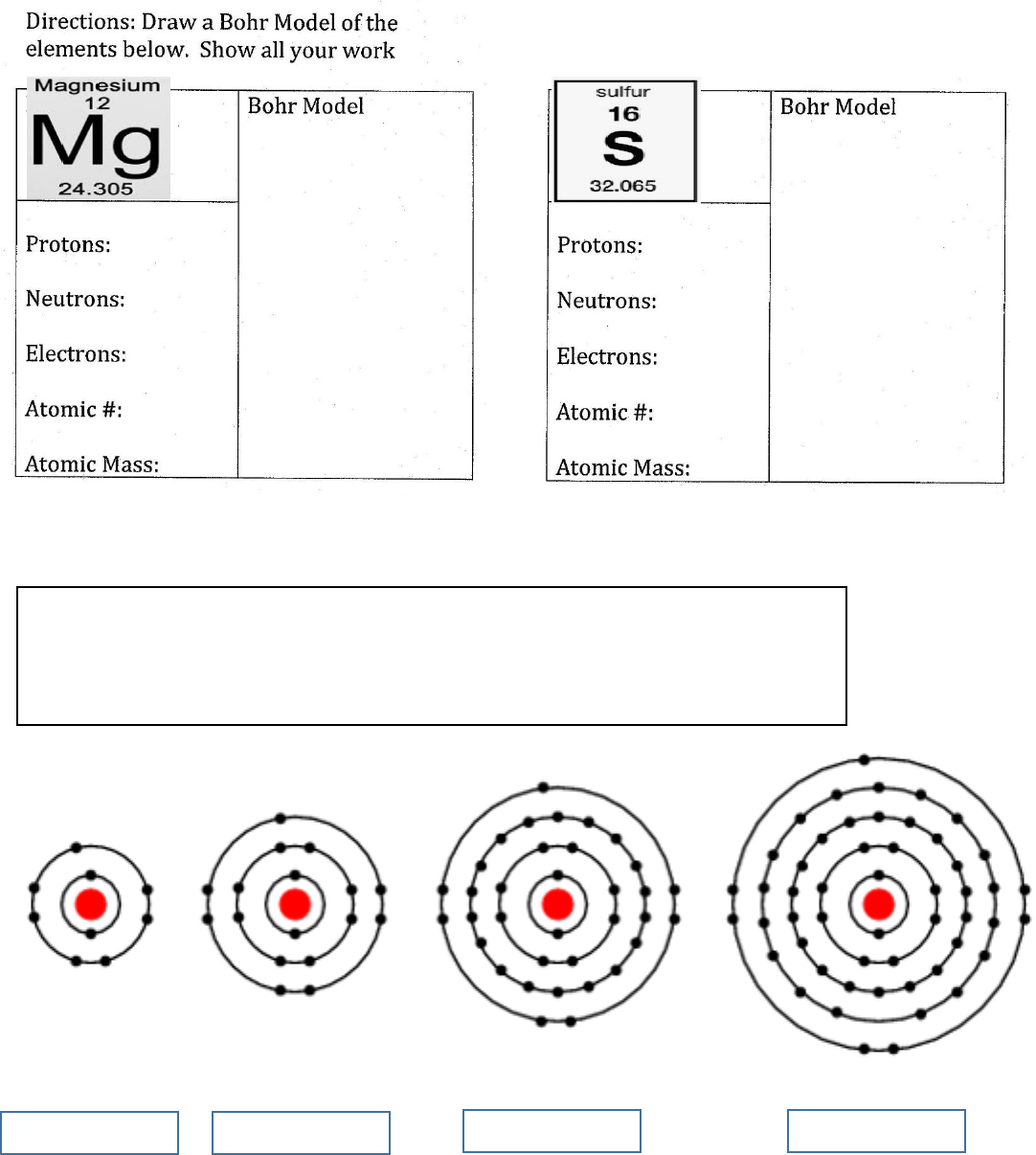
Identify each of the following. Which is which?
Iodine - Chlorine - Bromine – Florine
If you’re stuck count the shells &/or count valence electrons.
SCALE of ATOMS : 1mm = 1000 micronmeters (um)
1 micrometer = 1000 nanometers (nm) no ruler? call it →→ 40 mm
Measure the atom’s electron shell diameter.
What is the scale of this model if this atom’s valence electron shell
is 0.2 nanometers in diameter.
1. Measure the atom’s diameter, WRITE here→ _____mm = 0.2nm
2. Set up a proportion & report what 1mm equals to scale in the box.
Think about it…. I telling you the whole atom equals 0.2nanomters but what about the nuclues in this model or
the distance between on electron shel and another???
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
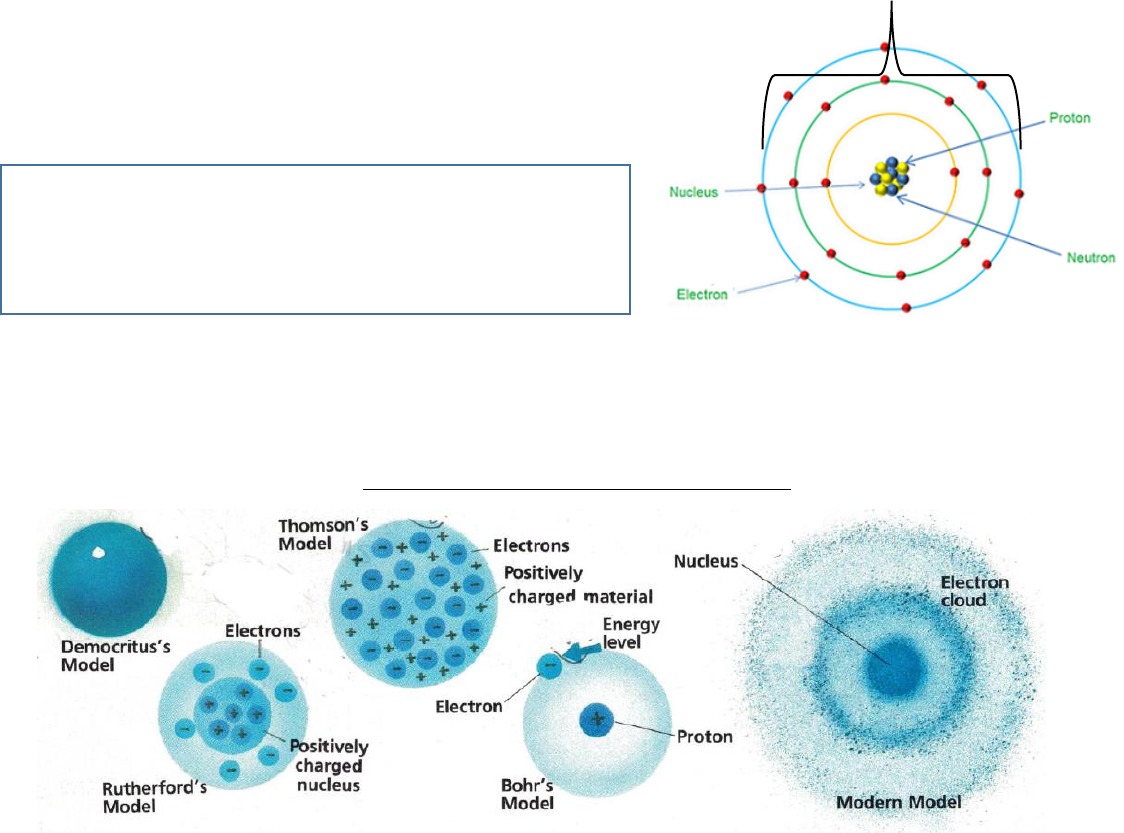
MODELS OF THE ATOM THROUGHOUT HISTORY
Fill in the physicists’ name for each of the below passages. (Hint see scientist names above)
_____________ was able to arrive at his model of the atom through careful observations using a
cathode ray tube. He called it plum pudding; positive pudding with negative electrons scattered
throughout.
A. Dalton B. Thomson C. Rutherford D. Bohr
_____________ utilized radioactive decaying material to fire alpha particles at a sheet of gold to
arrive at his model. Most of the alpha particles went right through. A few smashed into a densely
packed positive nucleus.
A. Dalton B. Thomson C. Rutherford D. Bohr
_____________ model paved the way for the present day Modern Model of the atom. He and others
proposed electron energy levels or quanta to explain the structure of the atom.
A. Dalton B. Thomson C. Rutherford D. Bohr
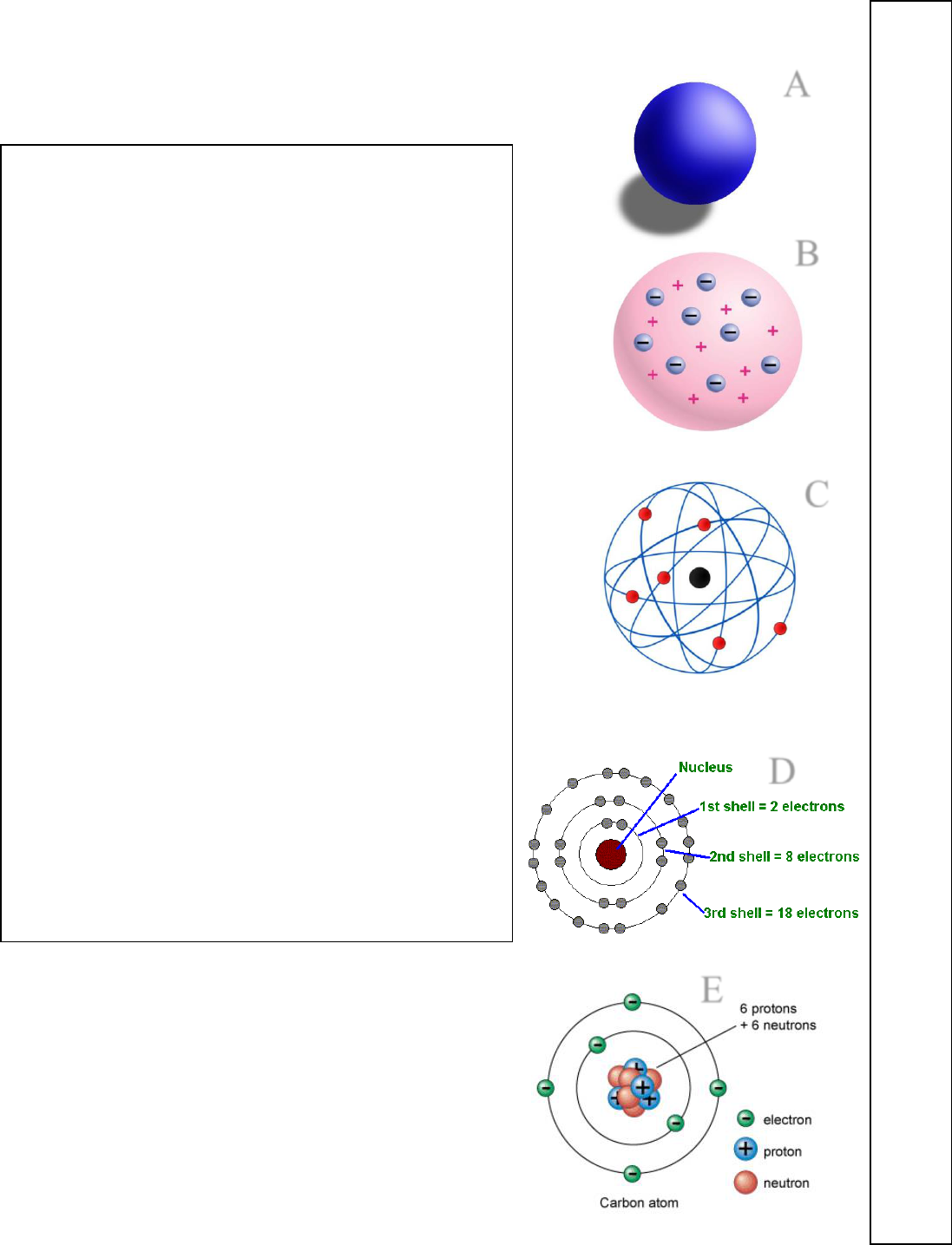
The Atomic Models - What were the major discoveries that each of the following
atomic models represented in its day?
MATCHING
WRITE LETTERS A-E ON THE LINES BELOW
Refer back to classwork, lab and notes for help.
______ The nucleus is discovered. The atom is found to be
mostly empty space. The nucleus is discovered to be an
extremely small dense and positively charged region.
______ The atom is found to be divisible, not indivisible as
had long been thought. The electron is identified as a discrete
part of the atom with a negative charge. The model is
described as “plum pudding”.
______ The remaining unexplained mass of the atom is
explained with the discovery of the neutron.
______ For the first time, specific elements are identified by
atomic mass - hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus
and carbon. Atomic structure still however unknown.
______ Quantum theory is adopted to explain electron levels
and the structure of the atom. The proton also becomes a
well-defined particle during this time period.
John Dalton
----------------
J.J. Thomson
-----------------
Ernest Rutherford
-------------------
Niels Bohr
-------------------
James C
hadwick
1766
-1844
Late 1800s
1871
-1937
Early 1900s
1921
-1935
A
B
C
D
E
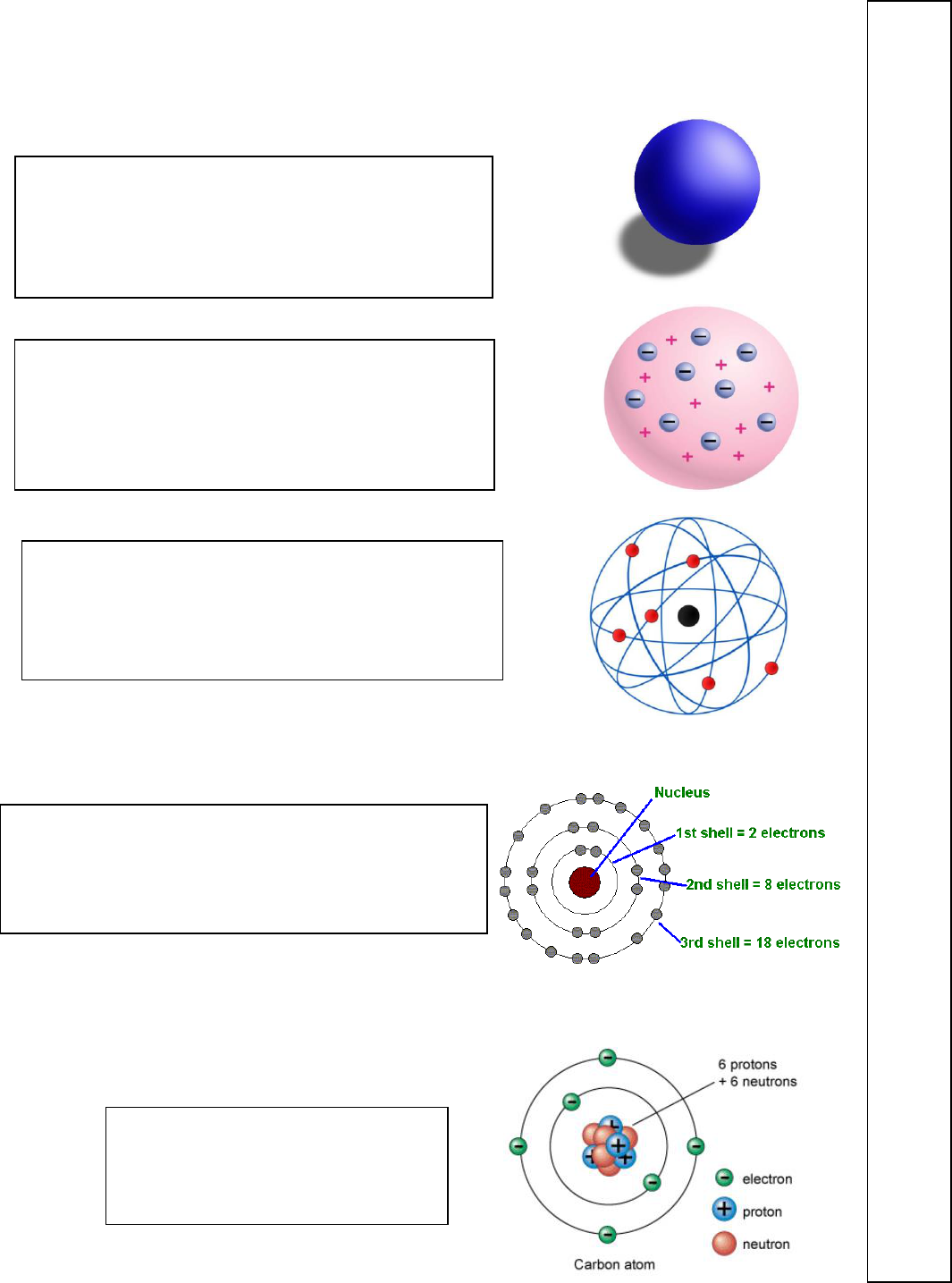
The Atomic Models - What were the major discoveries that each of the following
atomic models represented in its day?
Can you label 2-3 keys features in each diagram.
Dalton identifies for the first time specific elements by
atomic mass - hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur,
phosphorus and carbon. Atomic structure still however
unknown.
The nucleus is discovered. The atom is found to be
mostly empty space. The nucleus is discovered to be an
extremely small dense and positively charged region.
Rutherford
The atom is found to be divisible, not indivisible as had
long been thought. Thomson “Father of the Atom”
identifies the electron as a discrete part of the atom
with a negative charge.
Quantum theory is adopted to explain electron levels and
the structure of the atom. Niels Bohr provides
experimental evidence. The proton also becomes a well-
defined particle.
The remaining unexplained mass of the
atom is explained with the discovery of
the neutron by Chadwick.
John Dalton
----------------
J.J. Thomson
-----------------
Ernest Rutherford
-------------------
Niels Bohr
-------------------
James Chadwick
1766
-1844
Late 1800s
1871
-1937
Early 1900s
1921
-1935

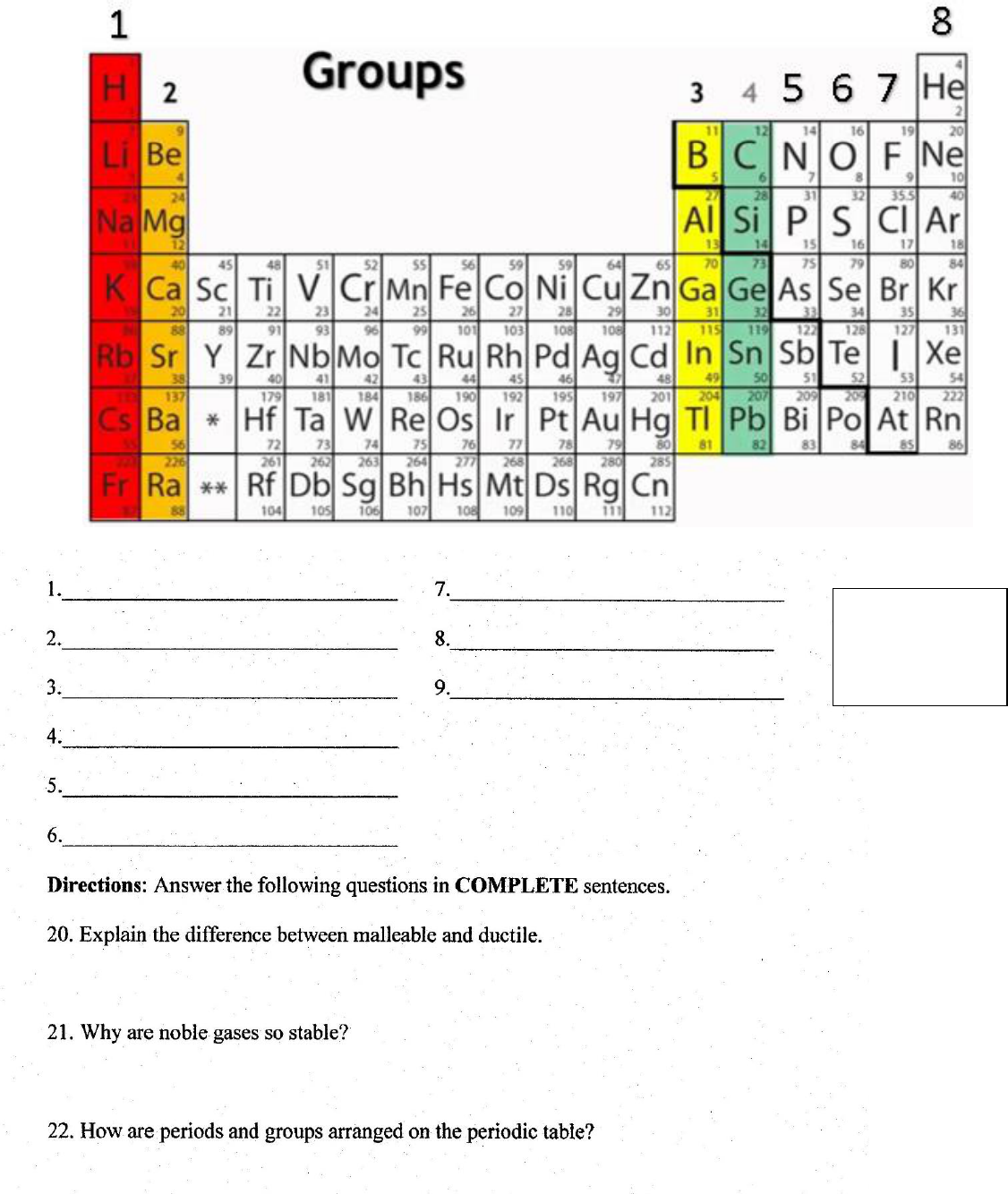
What are the names of each the following groups: 1-8
Read over Groups
and their
descriptions
previous page.


